DC-DC Converter: A Complete Guide for Energy and Electronics
What is a DC-DC Converter?
A DC-DC converter is a power electronics device that steps up or steps down the voltage of a DC power source while maintaining efficiency and stable output. It is commonly used in portable devices like laptops, mobile phones, and electric vehicles where different components require different operating voltages.
How Do DC-DC Converters Work?
DC-DC converters are electronic devices that convert one level of direct current (DC) voltage to another. They work by temporarily storing energy in inductors, capacitors, or both, and then releasing that energy at a different voltage. There are several types of DC-DC converters, including buck (step-down), boost (step-up), and buck-boost (step-up/down) converters, each designed to increase or decrease voltage as needed.
The basic operation involves switching elements like transistors turning on and off rapidly, controlled by a pulse-width modulation (PWM) signal. When the switch is on, energy is stored in the inductor or capacitor; when it turns off, the stored energy is transferred to the output. This process happens thousands or millions of times per second, allowing the converter to efficiently regulate and deliver a stable output voltage for various electronic applications.
Types of DC-DC Converters:
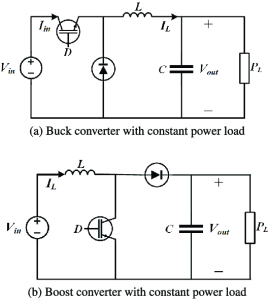
1. Buck Converter (Step-Down)
A buck converter reduces the input voltage to a lower output voltage. It works by switching a transistor on and off rapidly and using an inductor and capacitor to smooth out the voltage. It’s commonly used in battery-powered devices where lower voltages are needed (e.g., from 12V to 5V).
2. Boost Converter (Step-Up)
A boost converter increases the input voltage to a higher output voltage. When the switch is closed, energy is stored in an inductor. When the switch opens, this energy is released, adding to the input voltage to boost the output. It’s useful for applications like LED drivers or power supplies that need to raise voltage.
3. Buck-Boost Converter
This converter can either increase or decrease the input voltage, depending on the conditions. It inverts the polarity of the output in basic configurations. There are non-inverting versions too, which maintain the same polarity. It’s used where the input voltage may fluctuate above or below the desired output voltage.
4. SEPIC (Single-Ended Primary Inductor Converter)
A SEPIC converter can also step up or down the voltage like a buck-boost but provides a non-inverted output (same polarity as input). It uses two inductors and a coupling capacitor. SEPICs are good for battery-powered systems where input voltage varies above and below the required output.
5. Flyback Converter
The flyback is an isolated converter that can step up or down voltage and also provides electrical isolation between input and output using a transformer. It stores energy in the transformer during the switch-on phase and transfers it to the output when the switch is off. It’s widely used in low-power AC-DC and DC-DC adapters.
Each type is chosen based on the specific voltage conversion needs, efficiency requirements, and whether isolation is needed.
Applications:
1. Automotive
In modern vehicles, DC-DC converters are essential for powering different subsystems. For example, they step down the high-voltage battery (e.g., 400V in EVs) to 12V or 48V to run lights, infotainment, and control units. They also help manage power flow between batteries in hybrid and electric vehicles, improving efficiency and safety.
2. Hydrogen Energy Systems
DC-DC converters are used in hydrogen fuel cell systems to regulate and stabilize voltage from fuel cells, which can vary under load. These converters ensure a constant and usable voltage for powering electric motors or charging batteries in hydrogen-powered vehicles and backup power systems.
3. Solar/Wind Energy
In renewable energy systems, DC-DC converters adjust the variable output of solar panels or wind turbines to a consistent voltage for battery storage or grid integration. Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) converters are used to maximize energy harvest by adjusting the input voltage to the optimal point for power output.
4. Industrial Electronics
DC-DC converters power machinery, sensors, control units, and automation equipment in industrial environments. They provide reliable voltage levels for systems operating under harsh conditions and enable integration of different power sources and voltages in complex industrial setups.
In solar and wind systems, DC-DC converters play a vital role in stabilizing output. Learn how they power modern renewable energy grids.
Benefits of DC-DC Converters:
- Efficiency: They offer high efficiency (often above 90%) by converting power with minimal energy loss, especially compared to linear regulators.
- Voltage Flexibility: They can step voltage up or down to suit different components or systems.
- Compact Size: Modern converters are small and lightweight, making them ideal for space-constrained applications like portable devices and electric vehicles.
- Stability: They provide regulated and stable output voltage even when input voltage or load changes.
- Customization: Different topologies (buck, boost, etc.) allow tailored solutions for specific power needs across industries.
Limitations of DC-DC Converters:
- Complexity: Designs often involve complex circuitry with switching components, inductors, and controllers.
- Electromagnetic Interference (EMI): High-speed switching can generate noise that may interfere with other electronics.
- Cost: High-performance converters, especially isolated or high-power versions, can be expensive.
- Thermal Management: Heat generation at high power levels requires proper cooling to maintain reliability and efficiency.
In summary, DC-DC converters are powerful and efficient tools for power management but require careful design to mitigate noise, heat, and cost challenges.
Common Mistakes in Using or Designing DC-DC Converters:
- Poor Component Selection:
- Using incorrect or low-quality inductors, capacitors, or switching transistors can lead to inefficiency, overheating, or instability.
- Ignoring Switching Noise (EMI):
- Failing to account for electromagnetic interference can cause noise issues that affect nearby circuits or violate regulatory standards.
- Inadequate Cooling:
- Not providing enough heat dissipation (e.g., heatsinks or airflow) can cause the converter to overheat and fail, especially at high loads.
- Improper PCB Layout:
- Bad layout practices, like long traces or poor grounding, can increase noise, reduce efficiency, and cause instability in the circuit.
- Incorrect Feedback Loop Design:
- Poorly designed control loops can lead to voltage oscillation or slow response to load changes, affecting performance.
- Ignoring Input/Output Filtering:
- Lack of proper input/output capacitors or filters can cause voltage spikes, ripple, or instability.
- Mismatched Load Requirements:
- Not matching the converter’s output to the actual load demand may result in underperformance or damage to the load or converter.
Be aware of the common mistakes users make when selecting and implementing DC-DC converters.
Future Trends in DC-DC Converters:
- Higher Efficiency with GaN and SiC Technologies:
- Wide bandgap semiconductors like Gallium Nitride (GaN) and Silicon Carbide (SiC) are replacing traditional silicon components. They allow higher switching frequencies, lower losses, and better thermal performance—ideal for high-efficiency, compact designs.
- Smaller and Lighter Designs:
- With advancements in materials and integration, future converters will continue to shrink in size while maintaining or increasing power capacity. This is crucial for electric vehicles, drones, and wearable tech.
- Digital Control and Smart Monitoring:
- More converters are integrating digital controllers and telemetry features for real-time monitoring, fault detection, and adaptive power management, enhancing reliability and performance.
- Integration with Renewable and EV Systems:
- As demand for solar, wind, and electric vehicles grows, converters are evolving to support dynamic power sources, faster charging, bidirectional power flow, and grid interaction.
- Wide Input Voltage Range and Modular Designs:
- Future designs will offer flexible input ranges and modular architectures, making them easier to customize and scale across different applications.
These trends point to smarter, faster, and more efficient power conversion—paving the way for advanced electronics, greener energy, and more compact systems.
Discover how DC-DC converters and rectifiers are evolving in the hydrogen fuel sector in this detailed article.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1: What is a DC-DC converter used for?
A: A DC-DC converter is used to change the voltage level of a DC power source to match the needs of electronic devices or systems. It can either step up (increase) or step down (decrease) the voltage, and is commonly used in applications like electric vehicles, portable electronics, solar power systems, and industrial equipment.
2: Is a DC-DC converter a transformer?
A: Not exactly. While both are used for voltage conversion, a transformer works with AC (alternating current) and typically provides isolation between input and output. A DC-DC converter works with DC (direct current) and may or may not use a transformer. Some types, like flyback or isolated converters, do include a transformer, but others (like buck or boost converters) do not.
3: Can I use a DC-DC converter for solar systems?
A: Yes, DC-DC converters are widely used in solar energy systems. They help regulate the varying voltage from solar panels, often through MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) to maximize efficiency. Converters ensure the output voltage is suitable for charging batteries or feeding into inverters for grid use.
4.What Does a DC/DC Converter Do?
A DC/DC converter changes one DC voltage level to another, either stepping it up (boost) or down (buck) to meet the requirements of different electronic components or systems. It ensures that devices receive a stable and efficient power supply, even when the input voltage varies. DC/DC converters are essential in everything from smartphones and electric vehicles to solar panels and industrial equipment.
5: Which device is used for DC-to-DC conversion?
A: DC-to-DC converters are built using electronic components like transistors (switches), inductors, capacitors, and sometimes transformers (in isolated designs). These components work together in controlled switching circuits to efficiently convert one DC voltage level to another.
6: What are the three basic DC/DC converters?
A: The three basic types of DC-DC converters are:
- Buck Converter – Steps down voltage (e.g., from 12V to 5V)
- Boost Converter – Steps up voltage (e.g., from 5V to 12V)
- Buck-Boost Converter – Can either step up or step down voltage depending on the input and load conditions
7: What is the function of the converter?
A: The main function of a DC-DC converter is to regulate and convert DC voltage from one level to another, ensuring that electronic devices receive the correct and stable voltage needed for proper operation. It helps optimize power usage, protect sensitive components, and improve system efficiency.
Conclusion
DC-DC converters are vital components in modern electronic systems, enabling efficient and flexible power management across a wide range of applications—from automotive and renewable energy to industrial and consumer electronics. With various types like buck, boost, and flyback converters, they offer tailored solutions for stepping voltage up or down based on system needs. While they bring many benefits such as high efficiency and compact size, proper design and component selection are crucial to avoid common pitfalls. As technology evolves, innovations like GaN/SiC semiconductors and digital control are shaping the future of power conversion, making systems smarter, faster, and more reliable than ever before.




